Develop with Hardhat
In this tutorial, you’ll go through the full process of developing, testing, deploying, and verifying smart contracts on the GIWA chain.
Requirements
Node v22+
Set up development environment
mkdir giwa-project
cd giwa-project
npx hardhat --init
npm install --save-dev @nomicfoundation/hardhat-verifygiwa_project/
├── hardhat.config.ts # project configurations
├── contracts # project source code directory
├── test # contract test directory
├── ignition # Hardhat Ignition deployment script
└── scripts # scripts for deployment / simulationConnecting Hardhat to the GIWA chain
Loading environment variables
Writing a contract
Writing tests
Deploying the contract
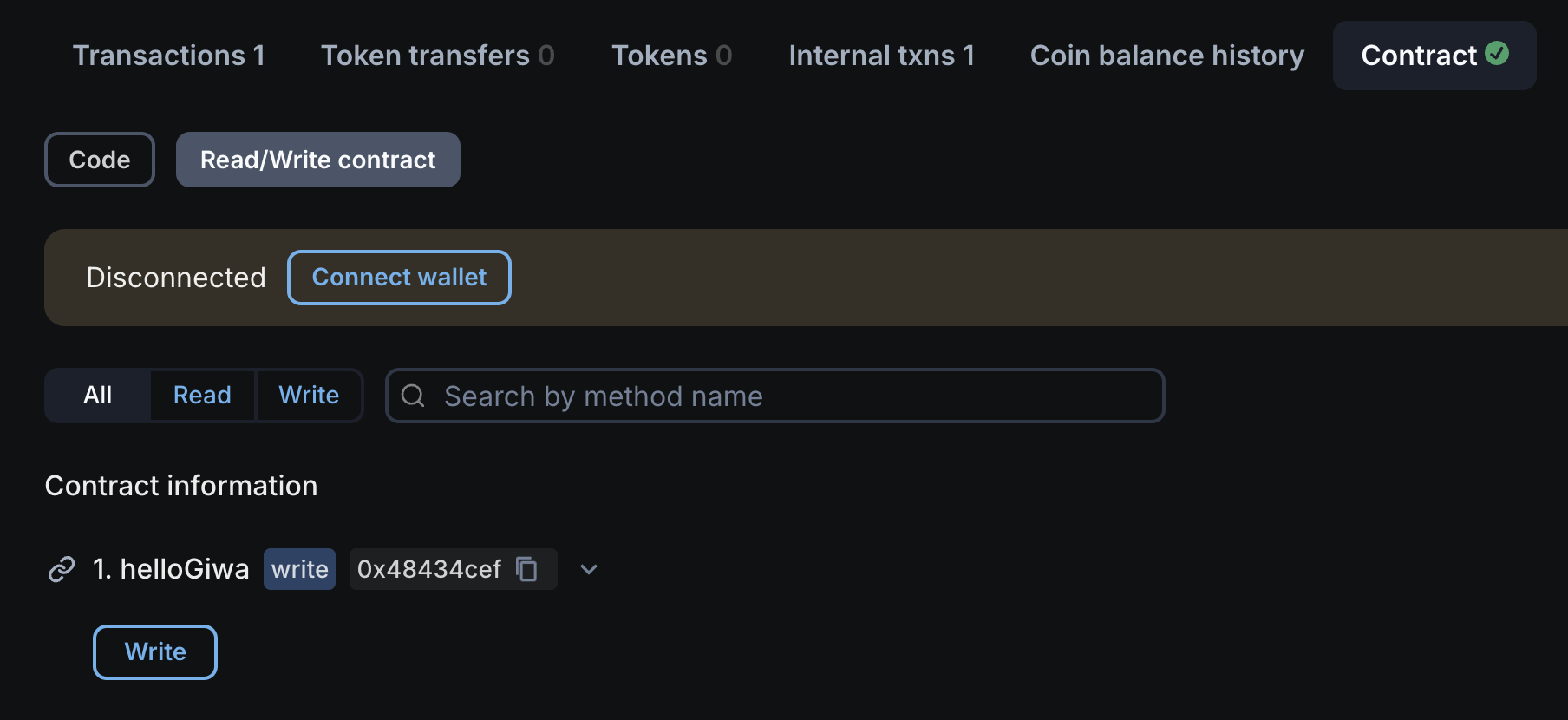
Verify and Interact with the contract in the explorer
Last updated